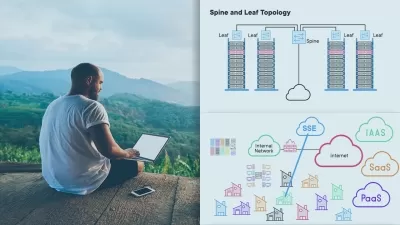
About Cloud ComputingLearn More
As companies around the globe shift their stack to the cloud, the demand for IT professionals with cloud computing skills has never been higher. In the past, IT roles were largely specialized: Linux admin, storage admin, network admin. Today, however, the shift to the cloud requires proficiency in all of these skills. Learn AWS, Azure, SpringBoot, and OpenStack with Udemy courses today and take your knowledge of cloud computing to the next level.
Sort by:
Sorting
The newest
Most visited
Course time
Subtitle
Courses
Subtitles

Ultimate AWS Cloud Practitioner Guide: Master AWS Fundamentals (2024)
13:17:03
English subtitles
01/09/2025
Frequently asked questions about Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing resources over the Internet. These resources include data storage, processing power, applications, physical servers, virtual servers, development tools, networking capabilities, and more. Cloud computing platforms help businesses build their complete infrastructure in a distributed fashion on the Internet instead of in their in-house data center. This offloads the costs of maintaining a company's own infrastructure to a cloud provider who will bill for only what they use. Cloud platforms offer elasticity to a business so that they can scale services based on workload. Virtualization in a cloud environment enables cloud platforms to provide more value by dividing physical hardware into virtual devices. The distributed nature of the cloud gives every user a low-latency connection, whether at the office or on the road.
Cloud computing has become the modern model for IT infrastructure, and there are many public cloud services to choose from. One popular cloud provider is Amazon Web Services or AWS. Amazon Web Services was the early leader in cloud computing services and currently a major provider of machine learning, database, and serverless cloud services. Microsoft Azure is another major cloud service. They provide their well-known Office suite of software including Outlook, Word, Excel, and PowerPoint using a software as a service (SaaS) model to their enterprise customers, as well as other general cloud computing services. The third-largest cloud provider is Google Cloud Platform. It works well for customers who want to integrate with Google's other offerings, like Google ads. Other cloud services available include Alibaba Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Oracle Cloud.
Cloud platforms provide a variety of computing services to their customers. They also offer storage for companies to store all data types in the cloud, including PDFs and public images, and private company files. Their granular security allows companies to set access rights down to a specific endpoint, data file, or user. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a common cloud service a company can use to manage operating systems, runtimes, data, and applications in the cloud. When a cloud provider offers a platform as a service (PaaS), they provide businesses with hardware that comes with pre-installed software, which helps developers to get started quickly. With software as a service (SaaS), the cloud provider manages software or a software suite for a business, and they just use it. Cloud platforms also offer serverless computing where a company doesn't manage the infrastructure, virtual machines, or servers. Instead, they deploy simple functions they can use on-demand.
Users are most likely to encounter cloud computing first as a form of storage. Today, most pictures, videos, and files on a mobile device (such as a smartphone or tablet) are stored in the cloud. This allows them to be accessed from anywhere. Enterprise applications such as Office 365 and Slack are also accessed via the cloud; in fact, most web applications and data storage today are cloud-based. The major advantages to the cloud are redundancy and stability, which makes the cloud particularly useful for data storage and data management. However, the cloud is also frequently used for its computing capacity. Video editors will edit videos on the cloud, and 3D artists will render simulations on the cloud. Other applications of the cloud include testing environments and big data analytics.
Nearly every IT career today will involve cloud computing. Some of the most popular careers that use cloud computing include systems administration, application development, and data analysis. There are also cloud-specific fields. Cloud architects design cloud computing infrastructure from the top down. Cloud developers make cloud computing applications. Cloud administrators run those applications, and cloud programmers will work under a developer to modify and manage the applications. There are managed services providers who specialize in cloud support, hiring cloud technicians. Additionally, there are fields that will use cloud computing for their systems, even if they aren't directly managing the cloud — most office workers today will use a type of cloud computing even if they don't realize it. For example, when office workers log into Office 365 or Slack, they use cloud computing technology.
There are public, private, and hybrid cloud solutions. Public cloud models are the most common. They are a cloud infrastructure that can be accessed from anywhere and stored in many servers rather than a single one. Usually, public clouds have several clients, all using the cloud service. But the cloud infrastructure is owned by the cloud services provider. Private cloud models are more specialized, private, and expensive. While it's still cloud-based (multiple computers sharing resources), only one client uses the cloud; this increases security. In this model, the private cloud operates much like a private server would. But unlike a private server, there are multiple computers, creating stability and redundancy. Finally, some hybrid models involve both public and private clouds, which work together to create a blend of efficiency and security. Some applications are stored on the public (shared) cloud in this model, while others are stored in the private (not-shared) cloud.
Cloud computing is considered stable, affordable, and scalable. But there are some disadvantages. When dealing with public cloud solutions vs. on-premise servers, public clouds may be slower and have greater levels of latency. When not properly secured, cloud services can represent security risks because of their expanded attack surface. And cloud computing, while overall more affordable, can have seemingly erratic pricing: because the company pays for the services it uses, it may not always know exactly how much it will pay. If the company needs to use more resources unexpectedly, costs can increase rapidly. Finally, cloud computing is still a relatively new technology, so it can be difficult to find specialized experts instead of those with a more general background, such as general experts in network infrastructure. Most cloud computing is still developed by large enterprises (AWS, Google, etc.), so it's less common that you will find a cloud computing expert at a small business.