About GISLearn More
Geographic Information Systems are tools used to analyze and present geographic and spatial data in the form of maps and layered visualizations. You can use GIS for monitoring agriculture, surveying, geology, and city planning.
Sort by:
Sorting
The newest
Most visited
Course time
Subtitle
Frequently asked questions about GIS
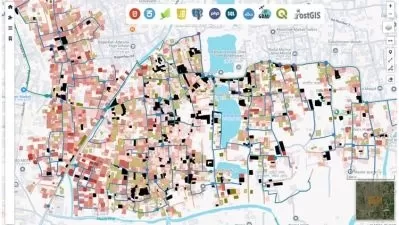
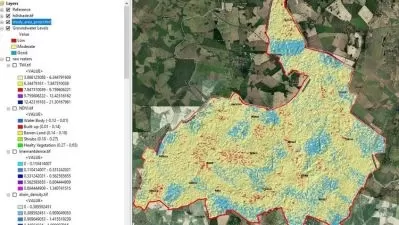
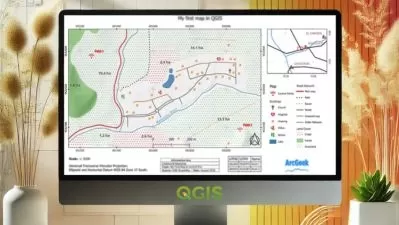
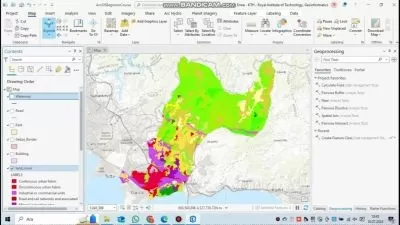
A geographic information system (GIS) is a system designed to collect, store, analyze, and process data connected to positions on the Earth’s surface. Spatial data can include natural features such as elevation and river flow, or it can include the built environment such as buildings and traffic networks. A GIS can be used to visualize spatial data in the form of customized maps that present datasets gathered from many sources. But the true power of a GIS is that it can process and analyze spatial datasets to answer questions and solve problems relating to the natural or built environment. GIS analysis can include distance measurements, statistical methods, and prediction and forecasting. While a GIS is used primarily to analyze and visualize spatial data, it can also process temporal datasets that contain information about data that changes over time within a certain area — for example, sun exposure throughout the year or traffic levels over a week.
The first use of GIS methods was in the 1800s when a physician mapped cases of a cholera outbreak in London to trace the source of the disease to a single well. Today, many professional fields can use a GIS to solve unique problems. Non-governmental organizations as well as governments turn to GIS to get statistical information on populations. Sales and marketing organizations use GIS to learn where their efforts will lead to the most success. Architects and civil engineers can use GIS to determine water drainage and wind patterns around a proposed building project. Other common GIS applications include urban planning, mining, agriculture, environmental management, and climate science. Almost every professional field uses spatial data in some way to make better decisions. This is why GIS professionals are in such high demand today.
GIS systems are commonly divided into five major components: hardware, software, data, people, and methods. A GIS can operate on a wide range of hardware types, from a stand-alone laptop to a centralized server. Using a centralized server means that connected devices use the server’s processing power to perform GIS tasks. GIS software provides an interface for performing GIS functions, including queries and visualization through maps. The most popular GIS software packages also include database management tools to organize source files. GIS data can come from various sources such as open-source and government databases, commercial data providers, or within the organization using a GIS. Typical GIS data include land features, gauge measurements, and property boundaries. People who use a GIS can use the other GIS components to solve a specific, real-world problem. Also, GIS methods involve the procedures and workflows used to solve problems using a GIS.